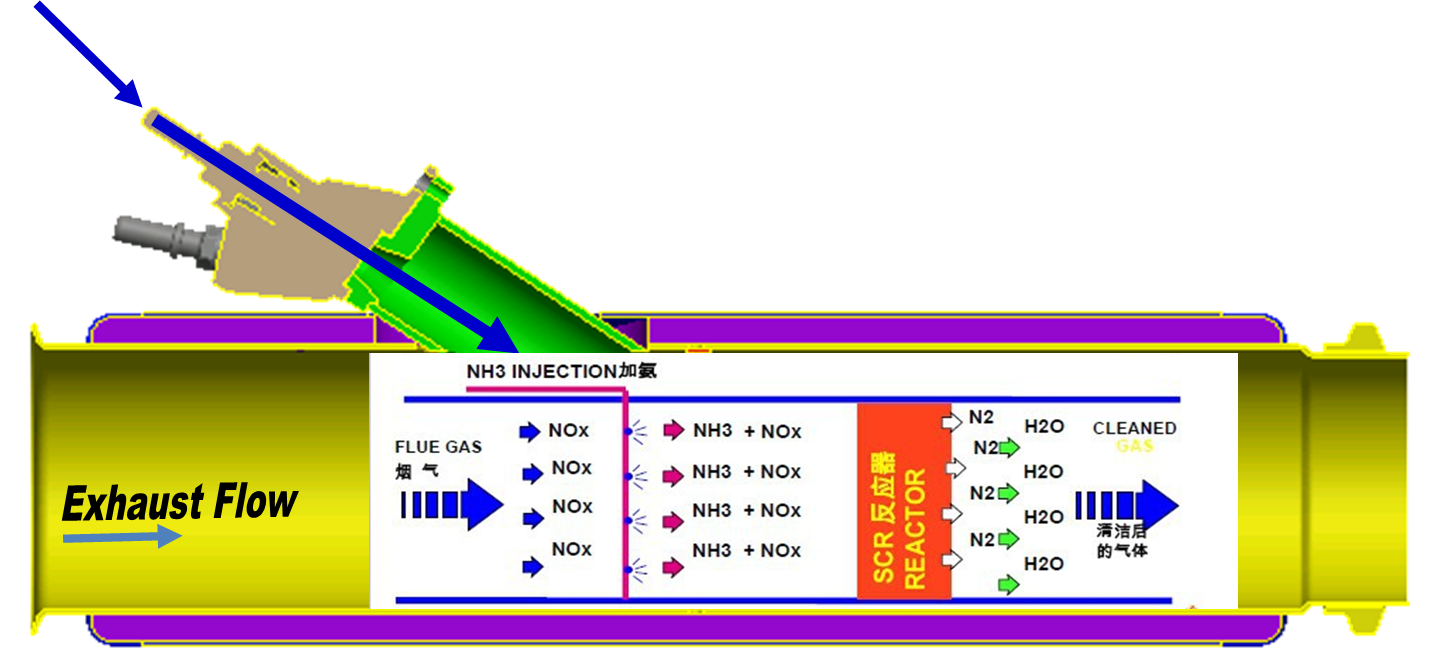
For truck owners, SCR is a very familiar word. Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) is an advanced active emissions control technology system used in diesel engines.
But do you know the function of SCR system?
There is a large amount of N2 and O2 in the air. When the diesel engine works, N2 reacts with O2 to produce NO, NO2, N2O3, and N2O5, etc. These are collectively called NOX, the main component of which is NO, accounting for 95%, with NO2 coming right after. NO is not very toxic, but can be oxidized to NO2. NO2 is a highly irritant and toxic gas in a brownish red color. Once inhaled, it combines with hemoglobin in the human body and reduces the oxygen transport capacity of the blood, leaving a harmful impact on the heart, liver and kidneys. NO2 can also cause plants to wither.
When the SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) system works, DEF (Diesel Exhaust Fluid), composed of 32.5% high purity urea and 67.5% deionized water, is injected into the catalytic converter, heated to 160℃ then decomposes into ammonia (NH3). NH3 then reacts with NOx, a harmful constituent of the exhaust, and produces harmless N2 and H2O via reduction reaction.